Global Digital Infrastructure Capacity Will Double in Less Than 5 Years, Possibly Triple in 10
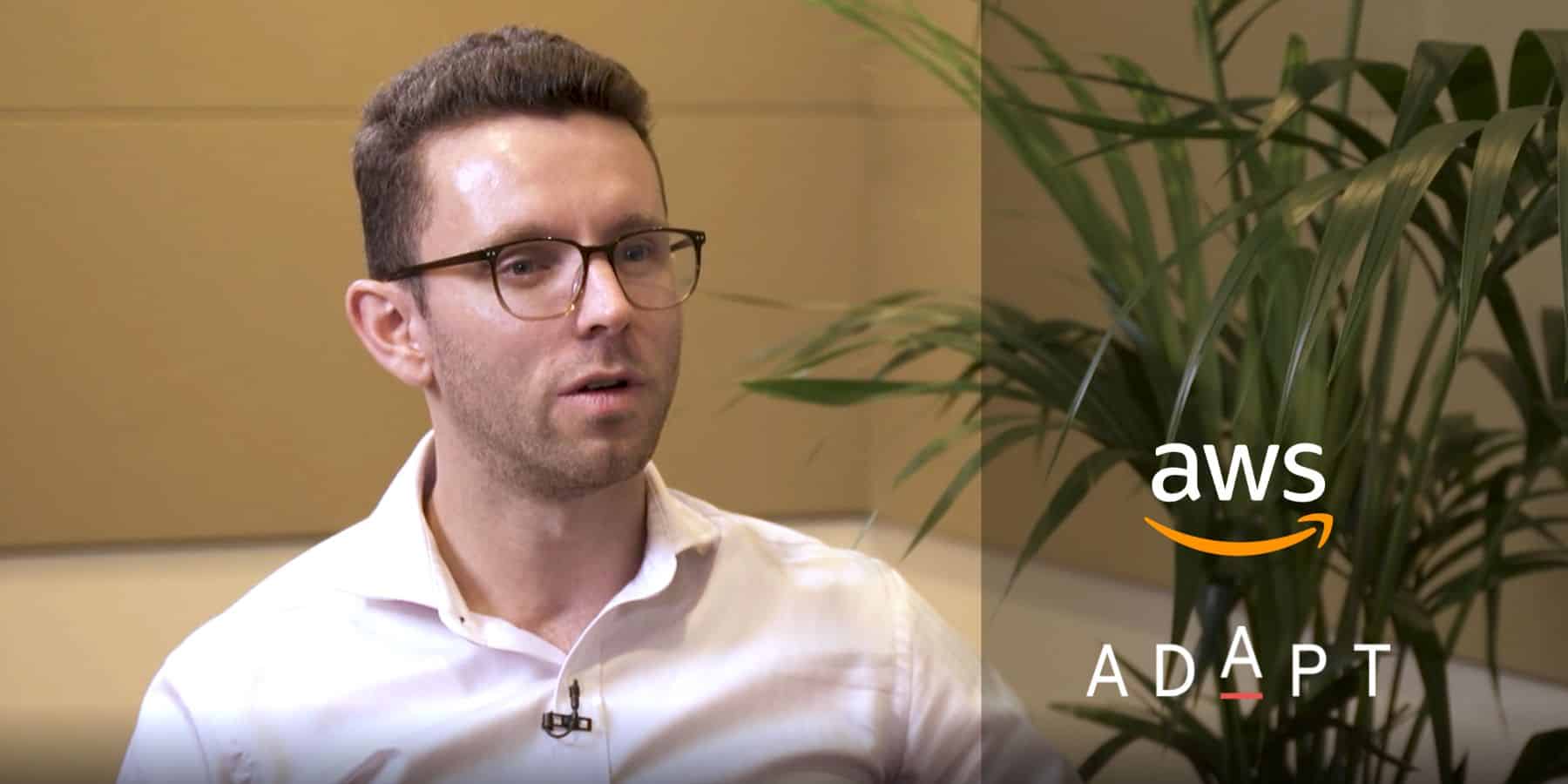
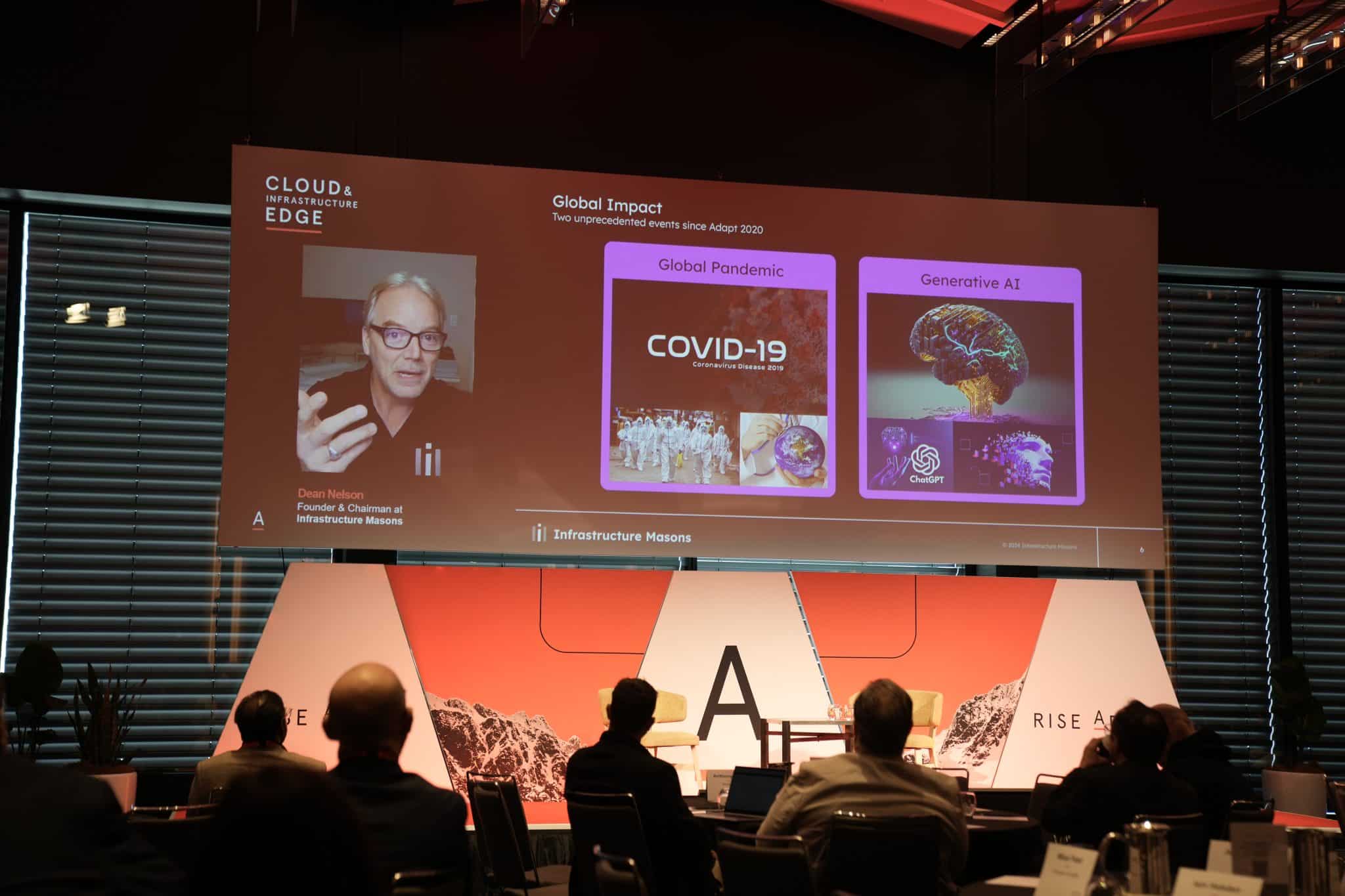
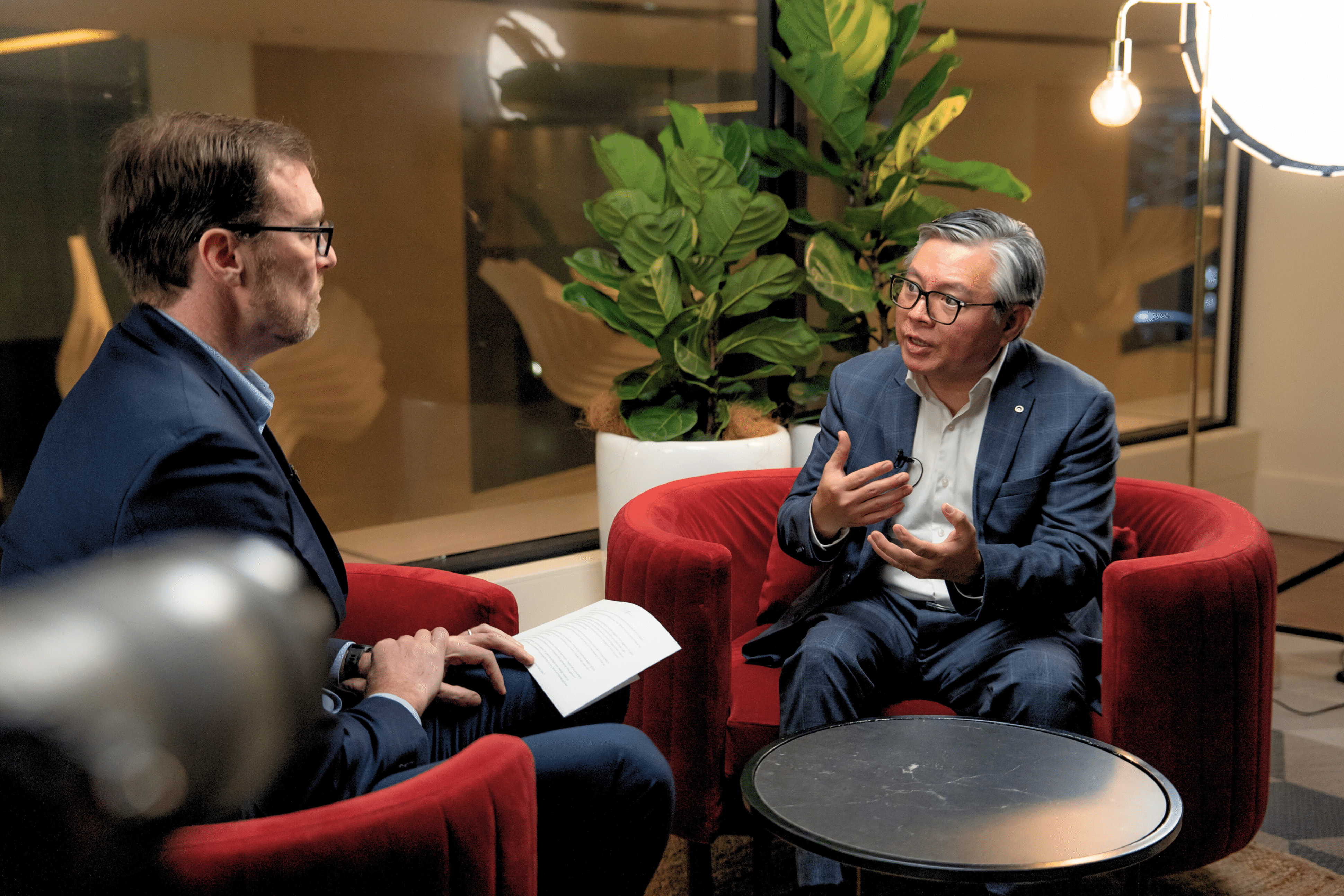
At Connected Cloud & DC Edge, Dean Nelson, Founder and Chairman at Infrastructure Masons, discusses the unprecedented challenges and growth within the digital infrastructure industry, emphasising the rapid expansion driven by the global pandemic and the rise of generative AI.At Connected Cloud & DC Edge, Dean Nelson, Founder and Chairman at Infrastructure Masons, discusses the unprecedented challenges and growth within the digital infrastructure industry, emphasising the rapid expansion driven by the global pandemic and the rise of generative AI.
Dean boasts 6000 global members and represents over $200 billion in digital infrastructure projects across 30 countries. The organisation unites the builders of the digital age, focusing on education, inclusion, innovation, and sustainability.
He presents insights from iMasons 2024 State of the Industry Report, detailing issues such as power access, workforce shortages, public perception, and sustainability.
The industry faces significant power and people shortages, with a 300,000-person shortfall expected by 2025 and a pushback from communities against data centres. The rapid growth poses a challenge to achieving net-zero goals, and Dean stresses the need to rethink strategies to balance growth with sustainability.
Collaboration is needed between major digital infrastructure companies, including AWS, Apple, Google, Meta, and others, to address the carbon debt associated with the rapid growth of digital infrastructure.
This initiative unites over 270 companies with a combined market cap of $8 trillion to focus on achieving net-zero carbon emissions.
They aim to decarbonise across three categories: building materials (embodied carbon), equipment, and energy sources.
The strategy includes aligning with the Open Compute Foundation for carbon accounting and promoting carbon labels on buildings and equipment.
Additionally, they advocate for greener concrete and environmental product disclosures (EPDs) to inform purchasing decisions.
They propose creating clean energy zones, where data centres are located near renewable energy sources, to facilitate sustainable growth.
The effort also includes a “social accord” to sustainably integrate digital infrastructure into local communities.
The overarching goal is to balance economic, ecological, and social factors to ensure sustainable development and positive community integration.
Key takeaways:
- Industry collaboration and decarbonisation: Collaboration among major digital infrastructure companies, including AWS, Apple, Google, and Meta, unites over 270 companies with a combined market cap of $8 trillion. This initiative focuses on achieving net-zero carbon emissions by decarbonising building materials, equipment, and energy sources, promoting carbon accounting and greener concrete.
- Sustainability and community integration: The strategy includes creating clean energy zones where data centres are located near renewable energy sources to facilitate sustainable growth. Additionally, a “social accord” aims to integrate digital infrastructure into local communities by balancing economic, ecological, and social factors to ensure sustainable development and positive community engagement.
- Industry challenges and workforce shortages: There are significant challenges faced by the digital infrastructure industry, such as power access issues, a 300,000-person workforce shortfall expected by 2025, and public pushback against data centres. There needs to be a rethink of strategies to balance rapid growth with sustainability goals amidst these unprecedented challenges.