How Australia’s Executive Leaders Are Harnessing Generative AI to Revolutionise Business and Innovation
Generative AI transforms Australian landscapes, urging ethical use. ADAPT's insights guide decision-making in this dynamic AI era.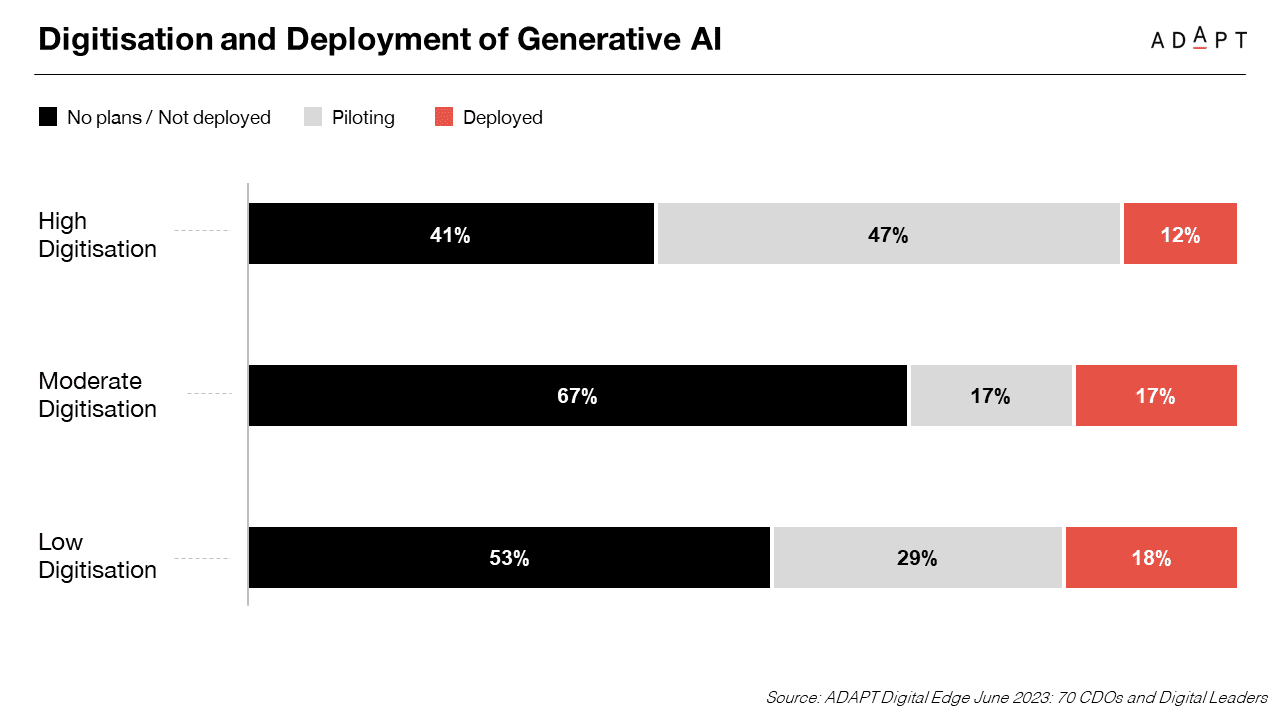
Generative AI, represented by models like ChatGPT, has emerged as a transformative force in Australia, driven by the wider adoption of AI/ML technologies.
The Australian Government is allocating a $17 million budget for the AI Adopt Program, establishing 5 AI Adopt Centres to aid small to medium enterprises (SMEs) in AI integration.
Accepting grant applications until January 29, 2024, with funding ranging from $3 million to $5 million per applicant, these centres aim to showcase AI capabilities, guide responsible adoption, and provide free specialised training to SMEs.
Aligned with the National Reconstruction Fund’s priorities, this initiative is a critical component of the 2023-24 Budget’s strategy to enhance competitiveness and productivity in Australia’s essential technology industries through widespread AI adoption.
The ADAPT Primer highlights its significance, focusing on the essential roles of quality datasets and Generalised, Pre-trained Transformers.
The report underscores the need for a shared language and responsible AI use, while addressing risks such as biases and data strategy challenges.
It encourages Australian organisations to consider their position in the global AI market, noting a lag in their AI sophistication.
The report lists five critical questions to help executives understand the differences between Generative AI and Discriminative AI, promoting informed discussions.
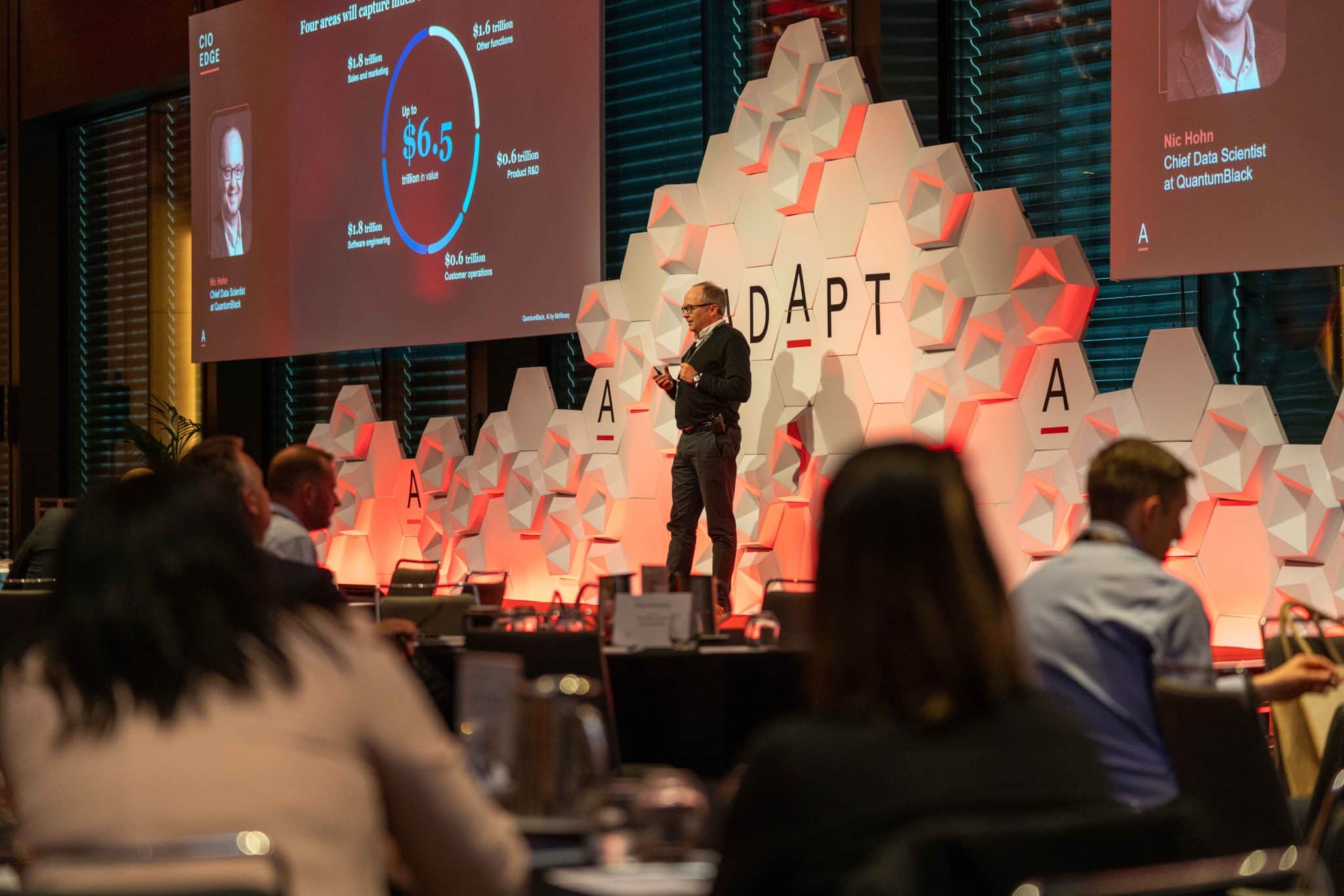
The rapid uptake of ChatGPT, with over 100 million users, underlines its impact on the market, urging executives to integrate this information into solid risk strategies.
Acknowledging philosophical questions about the future capabilities of Generative AI, the report suggests its significant commercial impact will be seen after 2027.
It showcases diverse applications, including real-world deployments like Deloitte’s Codex pilot, illustrating the breadth of possibilities.
Despite these opportunities, the report openly recognises the limitations of Generative AI, such as dependence on data and risks like deepfakes.
This highlights the importance of comprehensive risk assessments, ensuring Generative AI is responsibly adopted within a changing technology landscape.
Australian Enterprises Leverage Generative AI for Efficiency, Innovation, and Enhanced Customer Experiences
Generative AI, represented by models like ChatGPT, plays a significant role in the evolving landscape of Australian organisations.
This role is evident in the widespread adoption of AI/ML technologies, with 75% of entities embracing these advanced capabilities.
The insights come from ADAPT’s comprehensive analysis in the “Unlocking the Exponential Value of Generative AI” report.
Within this context, the report highlights the essential function of Generative AI in automating tasks, refining decision-making, and enhancing customer experiences.
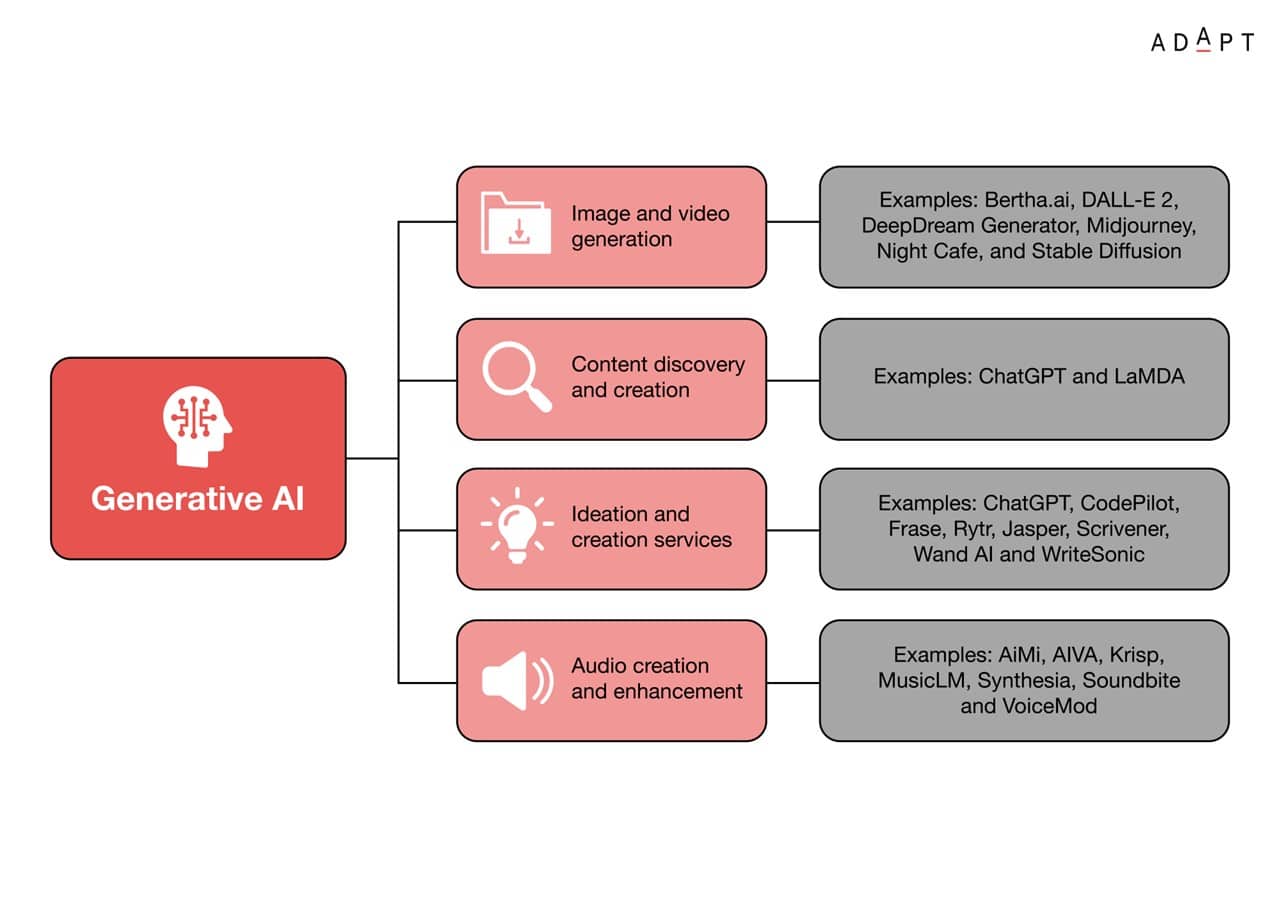
Despite challenges like complexity and skill costs, Generative AI is positioned to bring efficiency, innovation, and improved customer interactions to various industries, aligning with the evolving needs of Australian enterprises.
Taking a broader perspective, ADAPT’s analysis explores the landscape of emerging technologies, revealing that AI/ML is the second most prominent, with 39% actively deploying and 36% piloting these transformative technologies.
Within this trend, Generative AI, represented by ChatGPT, emerges as a significant contributor, anticipating a substantial role in the evolving technological trajectory.
Expanding the viewpoint to historical benchmarks of transformative technology adoption, the report notes that around 75% of Australian organisations actively deploy or pilot AI/ML technologies.
This aligns with global trends, positioning Generative AI as a notable force in this transformative journey.
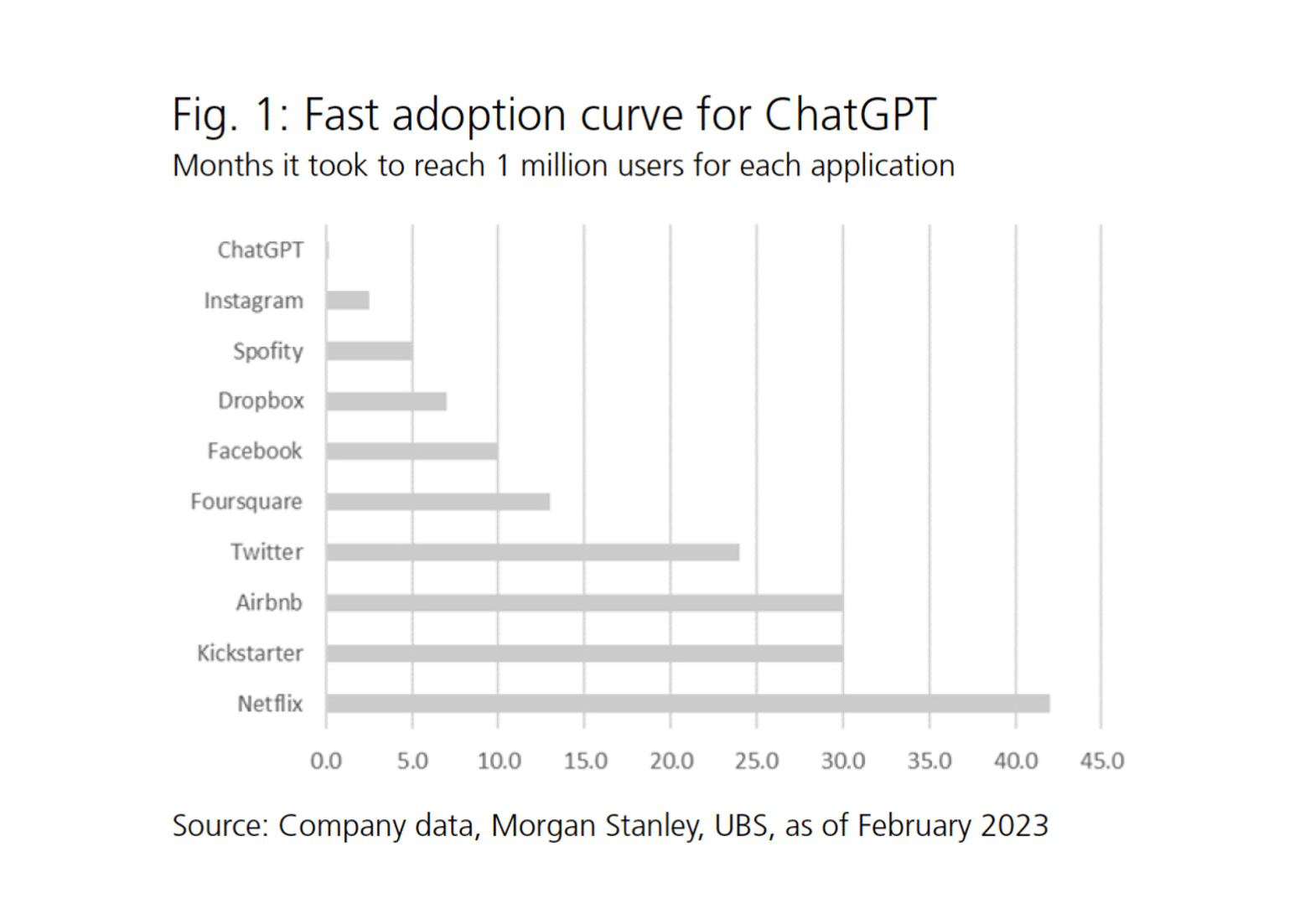
Conversely, the report highlights the swift rise of ChatGPT, demonstrating its quick adoption by reaching key milestones.
Surpassing 100 million users in just over two months, ChatGPT’s trajectory emphasises its potential and the rapid adoption typical of innovative technologies in today’s interconnected world.
Balancing Ethical, Privacy, and Bias Risks in Generative AI Implementation for Informed Decision-Making
Implementing Generative AI presents challenges related to ethics, data privacy, and biases, highlighting the need for human oversight to counteract model bias and out-of-date knowledge bases.
Privacy at Risk: The Truth Behind AI’s Collection and Use of Personal Information
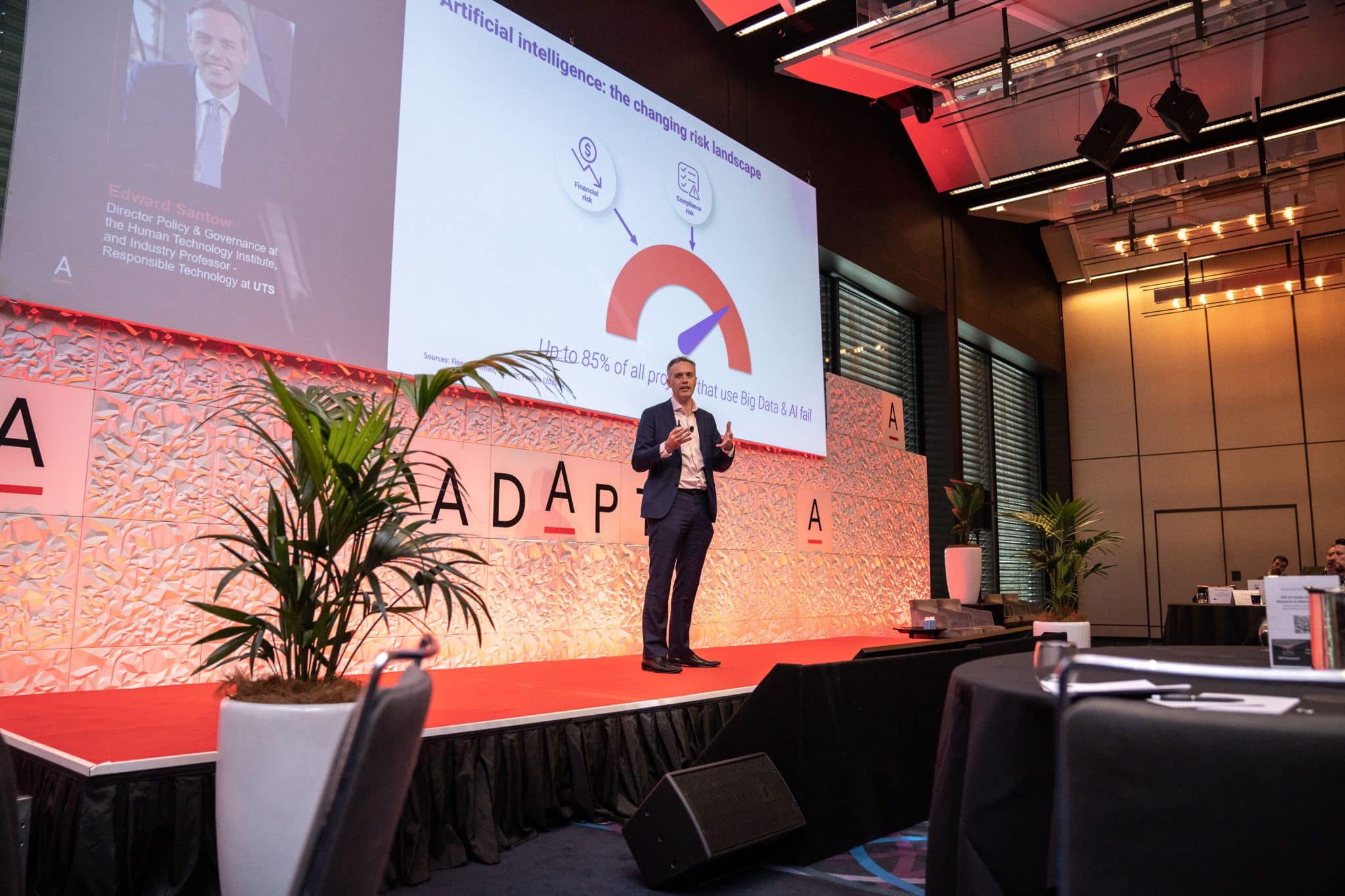

In Professor Edward Santow’s presentation on AI’s impact on the risk landscape, he emphasises the integration of human intelligence with machine capabilities as crucial for informed decision-making within sociotechnical systems. Challenges identified include:
- Algorithmic Bias Financial Risks: Particularly noticeable in financial services, algorithmic bias can unfairly disadvantage certain groups, like women.
- Reputational Risks: The growing tendency of consumers to switch providers due to perceived unfair use of personal data emphasises the increasing importance of fairness and accountability.
- Regulatory Recognition: The evolving AI field prompts recognition of the need for regulatory and legal adjustments.
Effectively addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive approach involving a deep understanding of AI operations, providing consumer guidance, data management, handling personal information responsibly, and addressing privacy concerns.
Beware of Relying Too Heavily on Automated Tools to Address Bias
Expanding on AI risks, Professor Ed Santow categorises them into legal, financial, and reputational dimensions, with a specific focus on algorithmic bias.
His caution against excessive automation emphasises the necessity for a balanced, analog approach, actively involving diverse stakeholders in governance.Key points include:
- Legal Risks: Regulators are applying existing laws to AI, necessitating thorough legal scrutiny.
- Financial Risks: Flawed AI tools can significantly impact an organisation’s financial health.
- Reputational Risks: Untrustworthy or ineffective technology usage can harm an organisation’s reputation.
- Algorithmic Bias Complexity: Ranging from questionable to constituting unlawful discrimination, algorithmic bias adds a layer of complexity to AI deployment.
- Caution Against Automation: Santow advises against overreliance on automated tools, advocating for a hands-on, analogue approach.
- Stakeholder Involvement: Highlighting the importance of a holistic approach, Ed emphasises the need to balance technical solutions with diverse human perspectives, emphasising the intricate nature of addressing AI-related challenges insightfully.
Unleashing the Power of AI Across Industries
The Possibilities and Power of AI
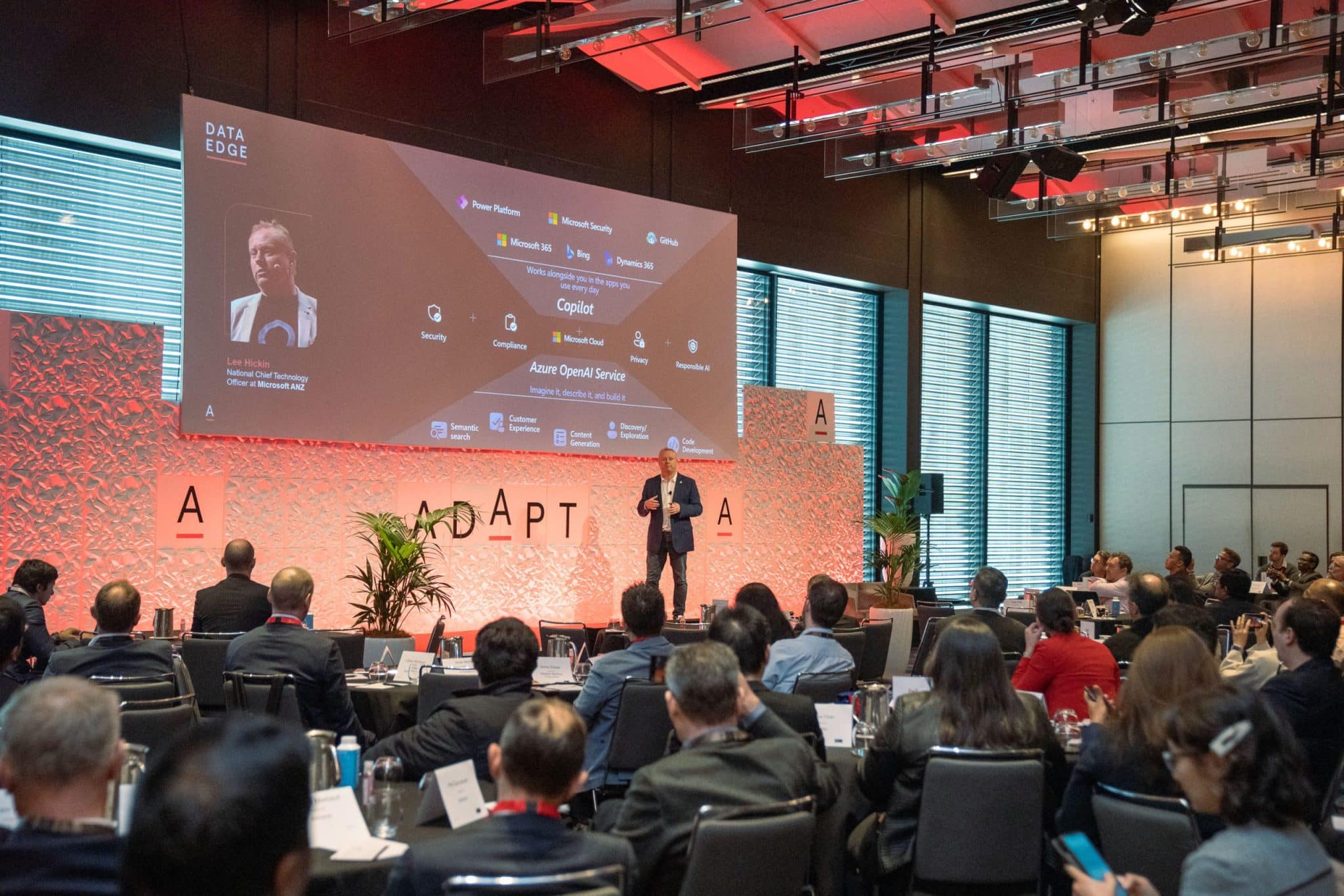
Lee Hickin from Microsoft delves into the transformative nature of AI, highlighting the shift towards natural language processing and the role of Microsoft Fabric in simplifying data integration.
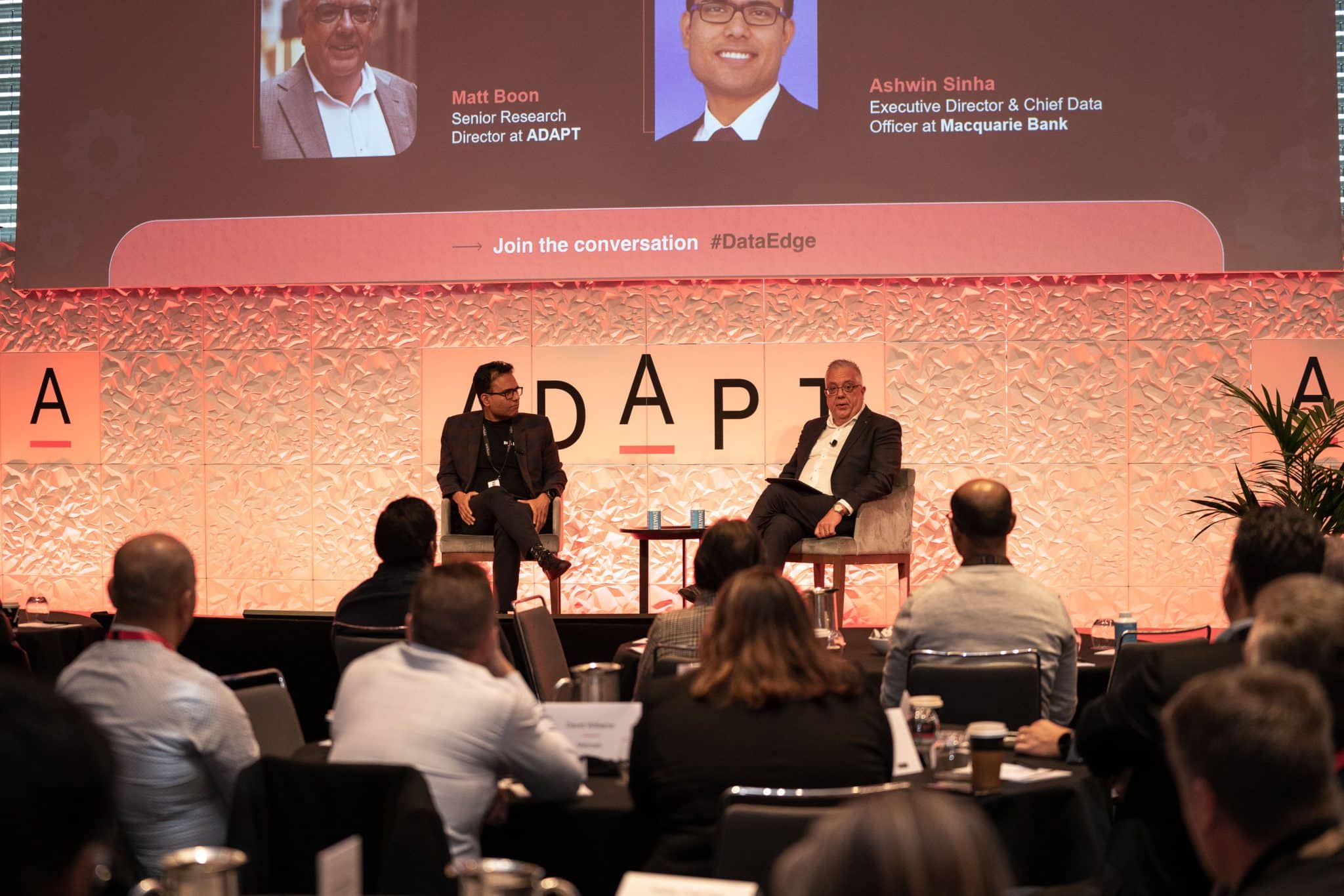
How Macquarie Bank Built an Efficient Data Infrastructure for Digital Transformation
Ashwin Sinha from Macquarie Bank points out the critical role of data quality and management in digital transformation.
Elements such as streamlined interfaces, technology modernisation, and data consolidation are explored to create a more efficient data infrastructure.
His presentation highlights continuous risk management, clear communication, and responsible AI implementation, considering governance frameworks comprehensively.
UTS’ Approach to IT Operations: Using Code and Automation to Improve Efficiency
With regards to the University of Technology Sydney (UTS), the emphasis is on their culture of continuous learning and digital collaboration for building high-performance teams.
This cultural shift is seen as foundational for driving corporate IT and innovation.
Adaptations during COVID-19, skills development through online platforms, and integration of Generative AI in operations contribute to UTS’s progressive approach, including leveraging infrastructure as code for IT automation.
Project Zero: Dell’s Pioneering Quest for a Zero Trust Future
Turning to Dell’s Project Zero, the focus is on the zero-trust security model inspired by the U.S. Department of Defense.

Dell’s emphasis on data protection over convenience suggests potential improvements in user experiences and cost reduction in secure systems.
This presentation also underscores the role of Generative AI in enhancing security, adopting an iterative and scalable deployment approach.
Taking Generative AI Beyond the Hype in Financial Services
The discussion in the financial services sector revolves around strategic generative AI implementation and its contributions to operational optimisation, robust risk management, and improved customer experiences.
Practical examples, such as Westpac’s streamlined tasks and financial institutions’ use for governance and fraud reduction, highlight tangible benefits.
CBA’s collaboration with H2O.ai is presented as an illustration of personalised services, emphasising the practical impact of generative AI.
From Data Chaos to Competitive Advantage
Shifting to Treasury Wine Estates, their success story focuses on collaboration and a consistent data culture as crucial elements in overcoming barriers to digital initiatives.
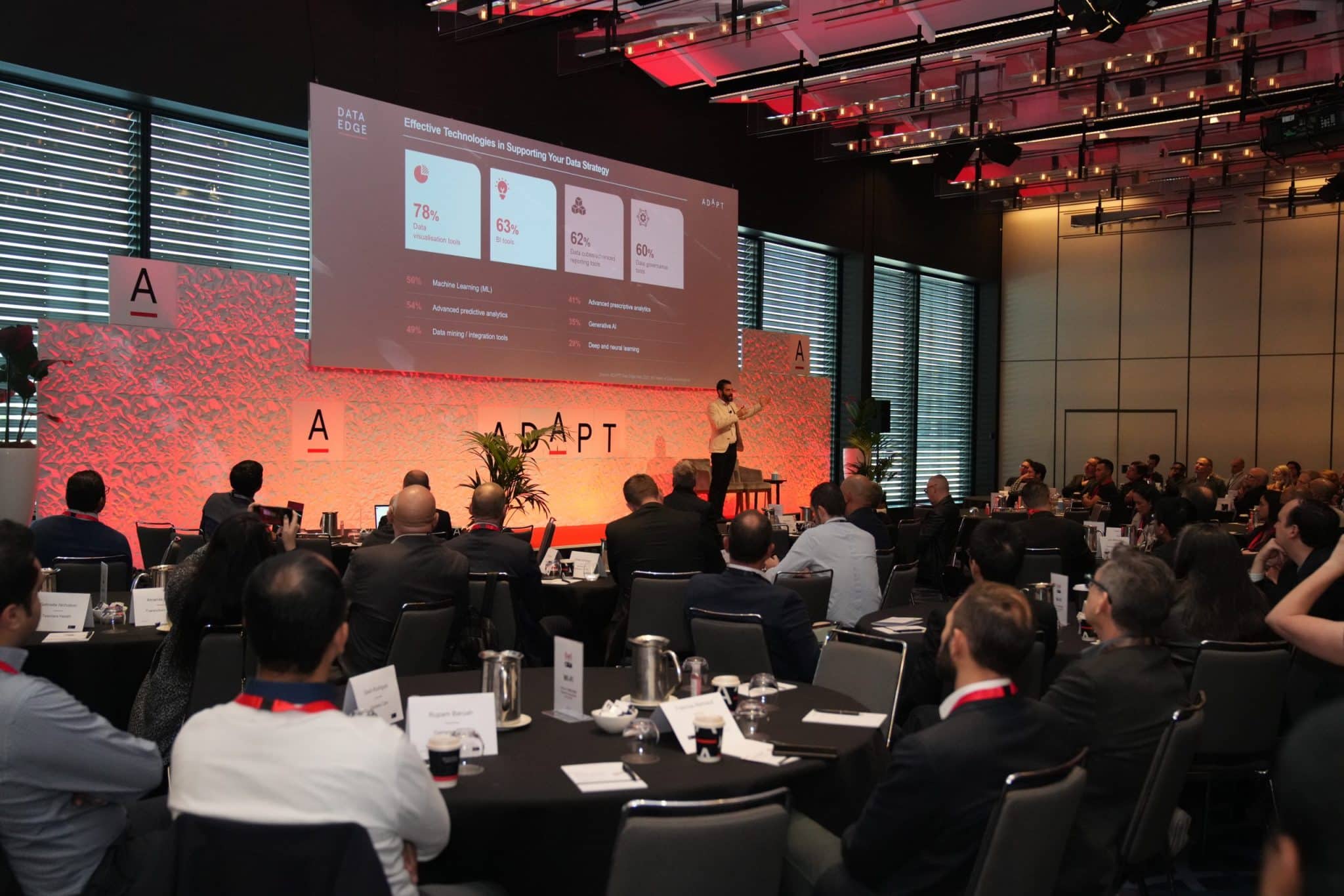

Strategies, including cross-training, closed feedback loops, and visualisation tools, are discussed for a competitive advantage.
ADAPT’s Head of Data and Analytics, Gabby Fredkin, shares the importance of a consistent data culture and collaborative efforts in realising successful digital transformations.
Navigate Generative AI Uncertainties with ADAPT’s Action Steps
In the face of Generative AI uncertainties, ADAPT’s study provides actionable steps for successful implementation.
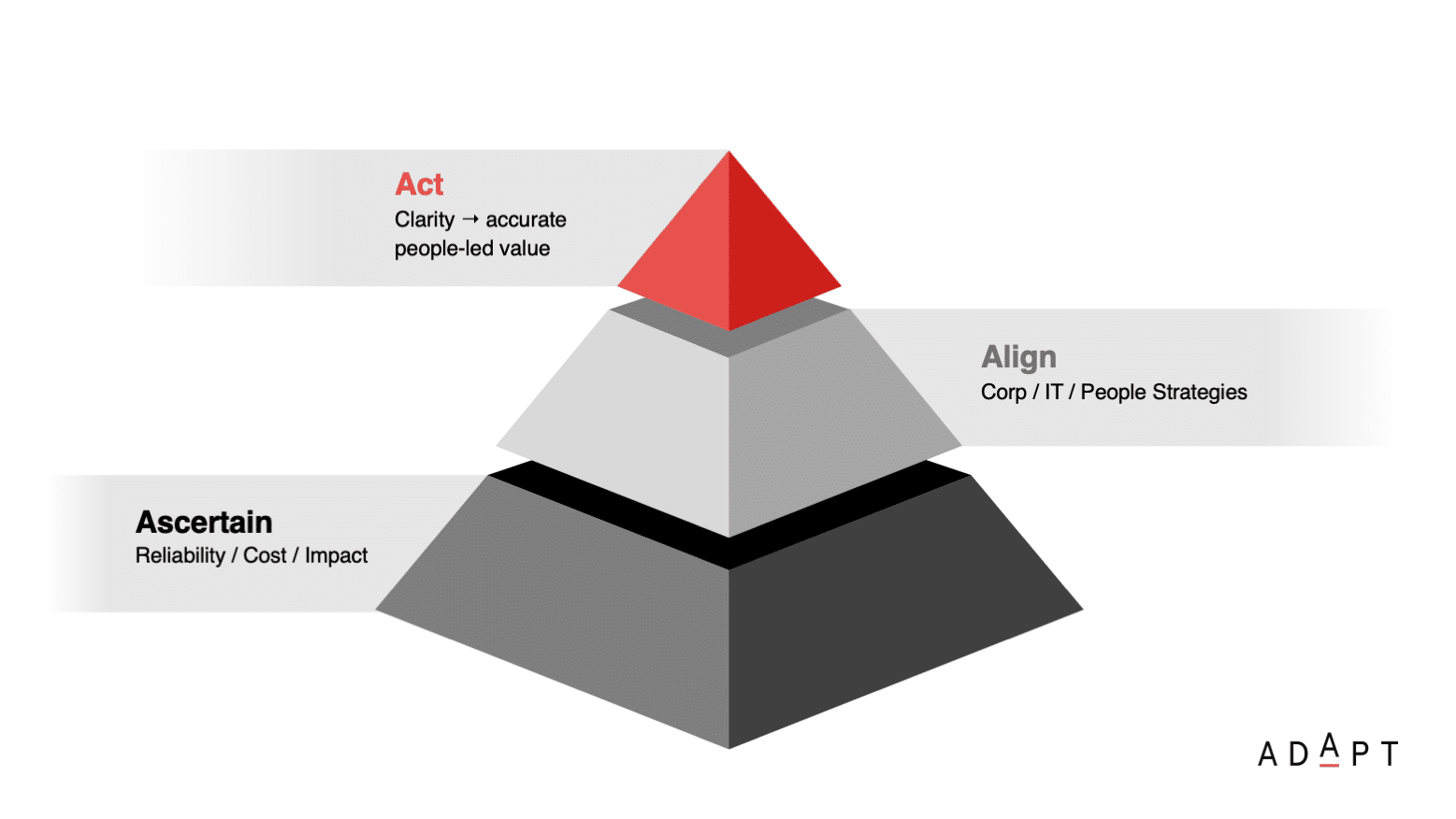
Key recommendations focus on measuring reliability, cost models, and impact, utilising metrics such as accuracy and scalability.
A SWOT analysis is instrumental in establishing a strategic baseline, aligning with sector dynamics and competitive environments.
Evaluation tools like ROUGE and Word Error Rate are crucial in measuring potential and natural impacts within the uncertain Generative AI landscape.
It is crucial to align implementation with corporate, IT, and people strategies.
Collaboration with key stakeholders, including CIOs, CDOs, CFOs, and CHROs, ensures a streamlined and value-driven approach.
There must be a connected strategy, with an alignment between the executive, cross-departmental teams, and technology strategies to accelerate value realisation amid the uncertainties of Generative AI.
Conclusion
The Generative AI landscape in Australia unveils transformative potential and challenges, emphasising responsible adoption and ethical considerations.
As organisations navigate this evolving terrain, synthesising insights, real-world applications, and cautionary notes provides a holistic perspective for informed decision-making in the dynamic realm of Generative AI.