Embracing the Future of Work with Generative AI
Embrace the Future of Work with generative AI. Corporate leaders leverage AI for innovation, efficiency & growth while navigating risks & ethical challenges.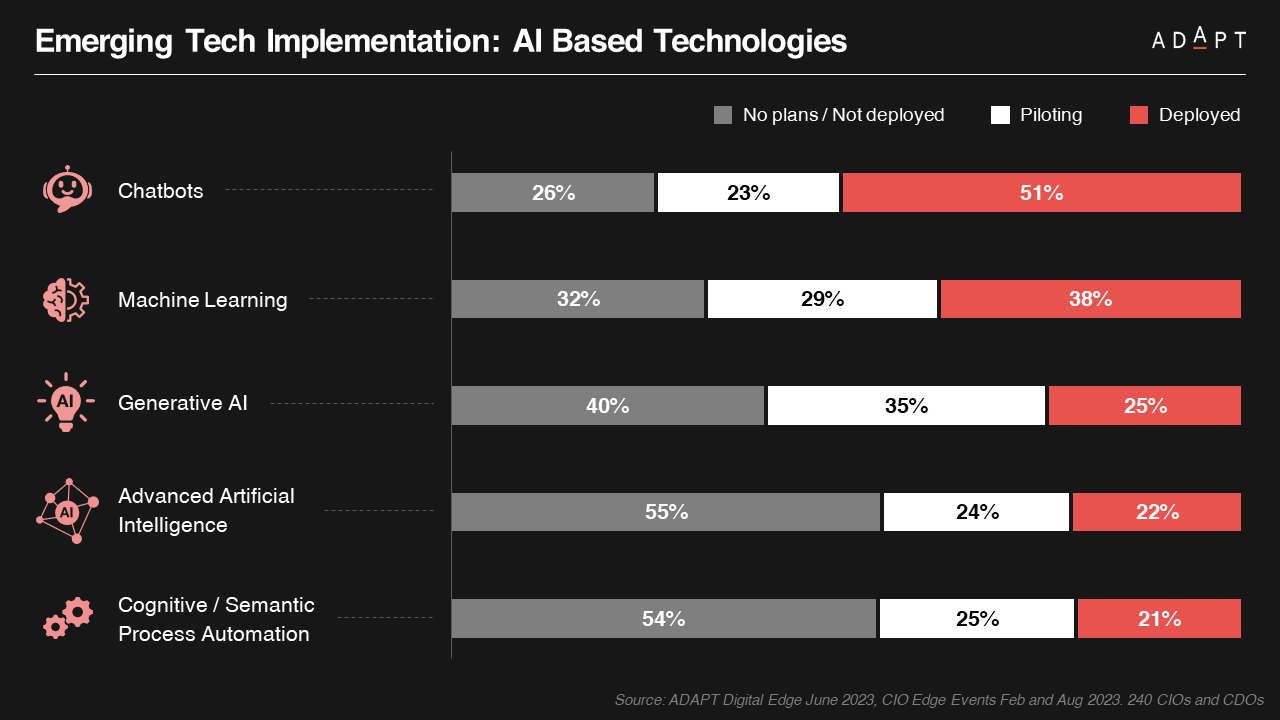
In the rapidly evolving business landscape, corporate executives have a transformative opportunity to leverage generative AI to drive innovation and efficiency within their organisations.
The integration of generative AI offers a range of benefits, including cost optimisation, improved decision-making, and enhanced efficiency.
By harnessing the capabilities of AI-driven analytics and automation, executives can proactively navigate competition and explore novel pathways for growth and success.
Nevertheless, these opportunities do not come without risks. The use of generative AI entails critical considerations such as data security and privacy, ethical implications, cyber security, and algorithmic bias.
75% of Australian Organisations Embrace AI/ML Technologies, ADAPT Reports
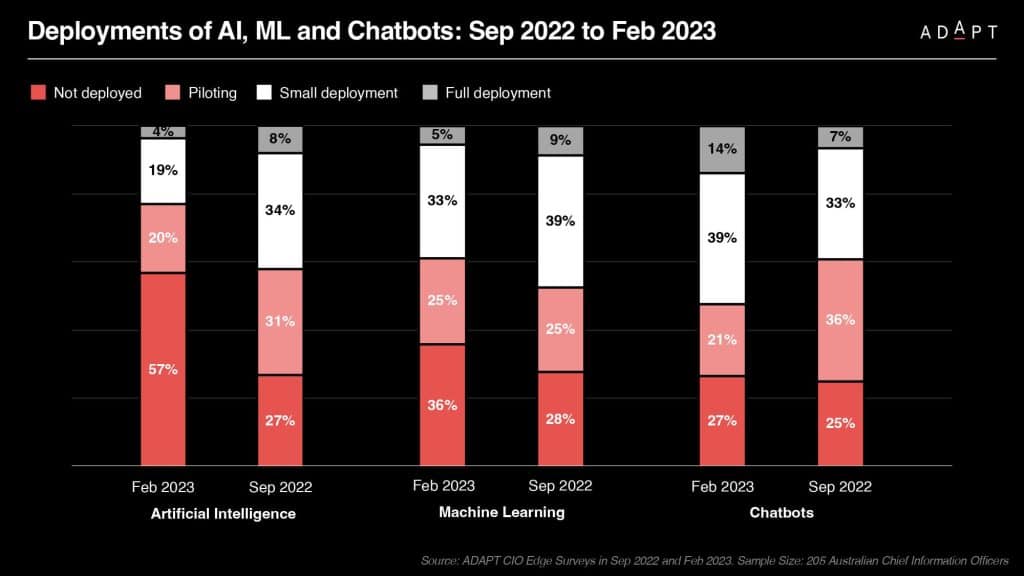
Analysis conducted for ADAPT’s Top Emerging and Value Priorities in 2023 has illuminated a noticeable increase in the adoption of generative AI by Australian organisations as they move into the year.
During this period, AI/ML emerged as the second most prominent emerging technology, with 39% of organisations actively deploying it and 36% piloting AI/ML technologies.
The trajectory is unmistakable: Generative AI is poised to play a substantial role in numerous organisations.
When evaluating how quickly innovations attain mass market adoption, it’s instructive to examine historical instances.
In 2021, AI technologies were adopted by 56% of organisations worldwide. Notably, markets like India (at 65%) and Developed Asia-Pacific (at 64%), which includes Australia and New Zealand, exhibited the highest adoption rates.
ADAPT’s ongoing research aligns with these trends, particularly within the local context.

ADAPT’s Market Trend reports on the business value of AI and the associated risks reveals that approximately 75% of Australian organisations are either deploying or piloting AI/ML technologies.
Taking a broader perspective by comparing the adoption timelines of transformative technologies, we can gain insights into the trajectory of generative AI. Here are some historical benchmarks:
- Fixed-line telephony gained 100 million users over a span of 75 years.
- The mobile phone achieved the same number of users in 16 years.
- The World Wide Web accomplished 100 million users in 7 years.
These pivotal transformations set the stage for subsequent digital advancements.
ChatGPT’s rapid rise is particularly noteworthy.
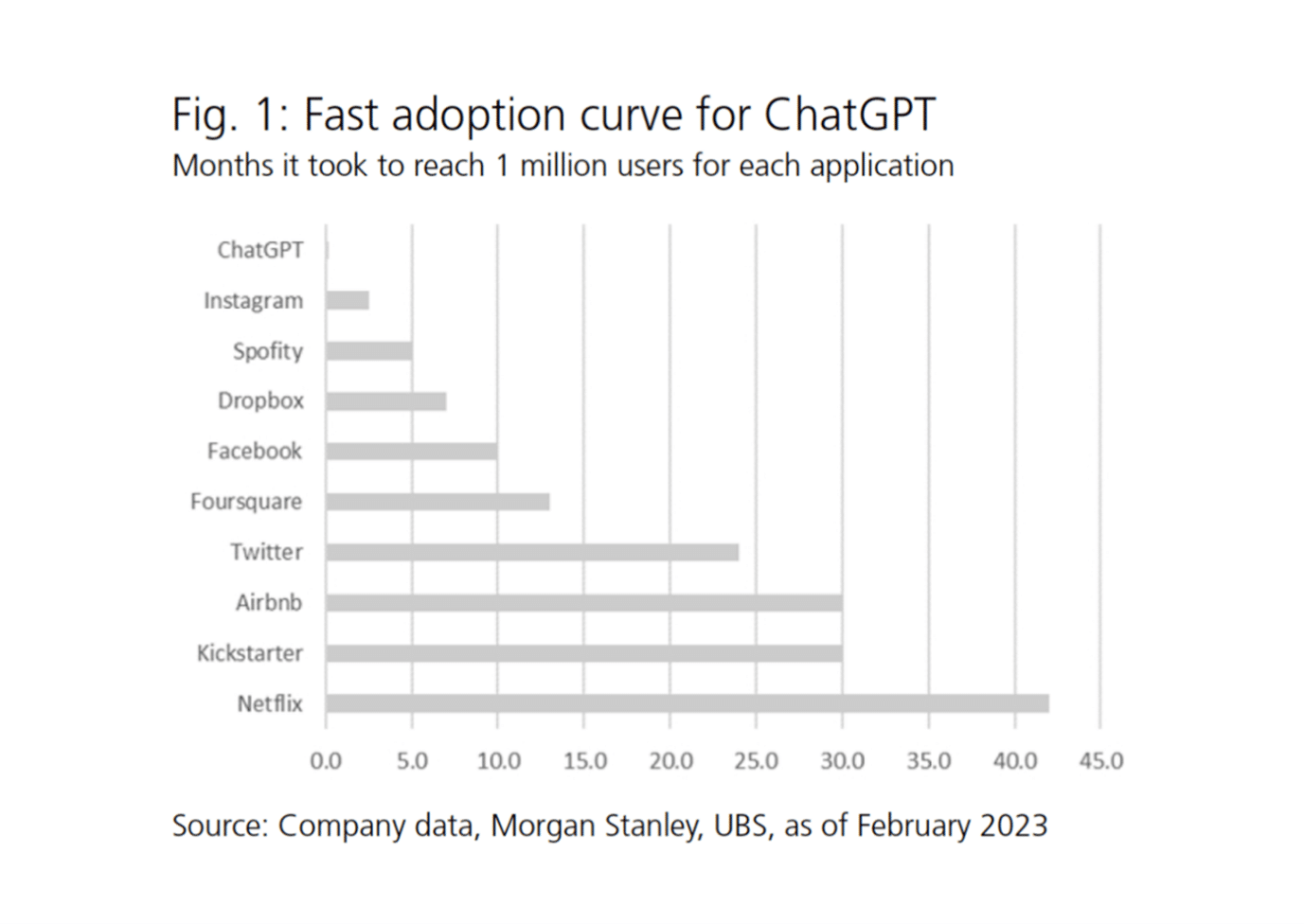
According to a UBS client note by Dennean (2023), the timeline for achieving 1 million users worldwide demonstrates the pace of its adoption:
- Netflix reached 1 million users in 3.5 years.
- Airbnb accomplished this in 2.5 years.
- Facebook achieved this milestone in 10 months.
- Spotify joined the list in just five months.
- Impressively, ChatGPT surpassed this mark in less than a week.
ChatGPT’s journey saw swift initial success and crossed the threshold of 100 million users in just over two months.
This remarkable trajectory highlights innovative technologies’ extraordinary pace and adoption potential in today’s interconnected world.
Generative AI’s Active Role in Driving Innovation and Efficiency Across Industries
Generative AI falls under the category of artificial intelligence technology capable of generating diverse forms of content, encompassing text, images, audio, and synthetic data.
Generative AI, on its own, does not inherently represent innovation. Utilising algorithms and statistical models, it processes a multitude of inputs to produce novel content combinations.
However, ensuring the credibility, value, and accuracy of these outputs necessitates human supervision.
As of the current state, the merits of generative AI primarily lie in its ability to synthesise, amalgamate, predict, and propose. It offers business users a way to streamline initial content generation and navigate through extensive information to discover potential novel prospects.
This assistance materialises in the form of prognostications regarding upcoming trends, patterns, and behaviours. Subsequent sections of this document furnish instances of use cases and cite real-world implementations.
Generative AI emerges as a catalyst for unprecedented growth and heightened productivity, ushering in a new era of operational excellence and innovation across diverse industries.
The ability of generative AI to automate repetitive tasks translates into increased operational efficiency.
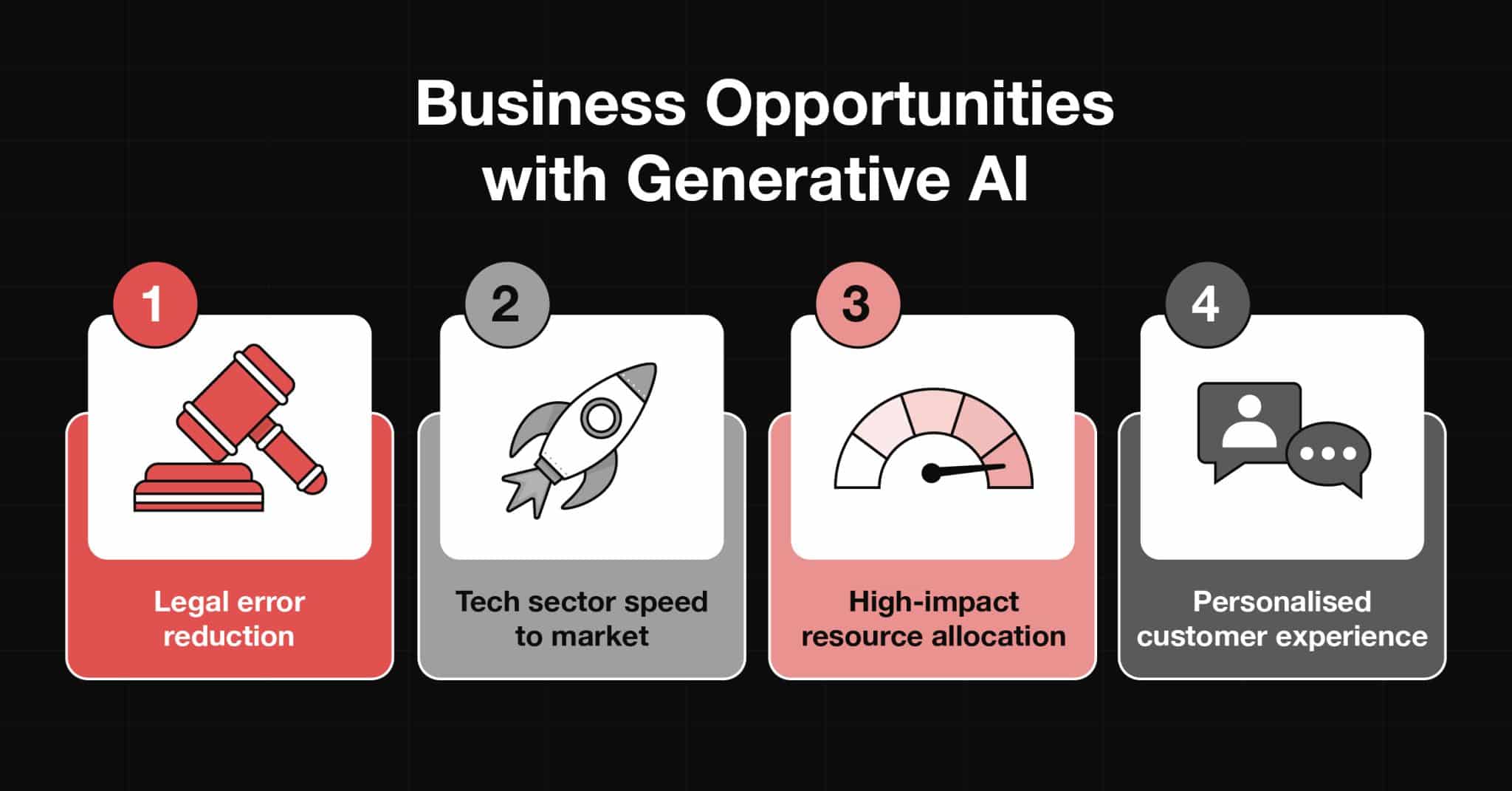
Organisations can redirect their human capital toward activities that drive growth and value by freeing employees from mundane duties. Some examples include:
- Legal firms can reduce error risks in contract drafting, allowing legal professionals to concentrate on strategic advisory roles.
- In the technology sector, the streamlined creation of product descriptions, market segmentation, and gap analyses empowers teams to respond to market demands and achieve growth opportunities swiftly.
- Armed with data-driven scenario analyses, financial services organisations can navigate market volatility with precision, steering resources towards high-impact strategies.
- Generative AI enhances growth prospects and decision-making efficiency, elevating customer experiences to unprecedented levels through personalised engagement.
By tailoring recommendations and interactions based on individual preferences and behaviours, organisations can foster customer loyalty and optimise conversion rates and cross-selling.
The fusion of generative AI with customer service chatbots results in consistently personalised responses, enhancing customer satisfaction and potentially leading to increased customer retention.
In the realm of application development and quality assurance, generative AI expedites processes. Standard algorithms are deployed faster, regression testing is automated and continuous integration and deployment are streamlined.
This leads to shorter development cycles and more efficient software releases, driving productivity gains and opening doors to innovation.
Moreover, generative AI’s dynamic pattern-matching capability introduces a new dimension to decision-making.
Unlike conventional historical trend analysis, it unveils fresh insights with the potential for substantial profitability.
Generative AI Empowering Insights for Strategic Growth and Operational Excellence
The potential that arises from effectively connecting decision-makers with their data has never been more pronounced.
The significance of business insights in understanding market shifts, exploring customer preferences, and subsequently guiding decisions is undeniable.
While there is still a need for human oversight, generative AI enhances decision-making by providing tools and insights that facilitate a more thorough analysis, a better understanding of trends, and the ability to predict potential outcomes.
When strategically harnessed and channelled through aligned corporate, people and data strategies, these insights become robust assets, capable of:
- Guiding diverse decisions: Insights are pivotal in shaping strategic, tactical, and opportunistic decisions, fostering informed actions at multiple levels.
- Facilitating growth planning: The ability to identify and predict future opportunities enables effective scenario planning, enhancing an organisation’s adaptability to changing circumstances.
- Optimising operations: Valuable recommendations derived from insights streamline operations, unlocking the latent potential within processes and human resources.
Microsoft’s AI Transformation Unveiled – Lee Hickin Highlights Profound Impact and Rapid Adoption
Lee Hickin highlights today’s profound impact and remarkable adoption of artificial intelligence (AI), with Microsoft leading the way in this transformation.
He described how AI, a cornerstone of Microsoft’s approach, has become integral to our lives, transforming how we interact with technology and manage data.
- ChatGPT growth rate: Lee shared a fascinating statistic that exemplifies Microsoft’s rapid adoption of AI tools. The growth rate of ChatGPT, a large language model, was an astounding 3.8% per day, reaching an estimated 300 million users. This statistic underscores Microsoft’s successful efforts to meet user demand and eagerness to engage with AI-powered interfaces.
- Data generation: Lee also highlighted the exponential growth in data generation, a phenomenon that Microsoft is actively addressing. He pointed out that each individual generates approximately 2 megabytes of data daily. When multiplied by the world’s population, this seemingly small number accumulates into a massive volume of data, demonstrating Microsoft’s recognition of the widespread adoption of technology and the increasing reliance on data-driven solutions.
- Email volume: Lee highlighted the staggering volume of communication data, a challenge that Microsoft’s AI-driven tools are well-equipped to manage. He mentioned that, as a society, we send around 332 billion emails daily. This statistic underscores Microsoft’s role in providing essential AI-driven solutions for managing and deriving insights from this overwhelming information.
Conclusion
As this trend gains momentum, it brings forth both opportunities and challenges.
Emerging possibilities are accompanied by potential obstacles, ranging from increased productivity, and malicious practices like deepfakes and phishing.
Organisations need to address these challenges proactively to harness the potential of generative AI.