Inside the Australian Market: Generative AI, Cyber Security, Cloud Migration, and Government Support
ADAPT's 2023 Trends Update: Review Australian organisations' cyber security progress, cloud & generative AI adoption, and Government IT support.
In January, ADAPT unveiled its top picks for the trends expected to make a big impact in 2023. Now that we are halfway through the year, let’s assess the current status.
Understanding cloud migration, government support for digital transformation, cyber security, and generative AI adoption is crucial for businesses.
Cloud migration enables seamless collaboration, optimises costs, and ensures long-term savings. Government support fosters innovation, economic growth, and job creation.
Cyber security protects data and customer trust.
Embracing generative AI accelerates enterprise success by unlocking new possibilities.
By staying informed about these trends, businesses can make strategic decisions to drive growth, and attract top talent, whilst maintaining customer trust and loyalty.
1. The generative AI revolution accelerates investments for enterprise success
In 2023, investments in AI/ML, particularly Generative AI, are accelerating and are at the forefront of emerging technologies for the year. They hold the potential to deliver substantial ROI for enterprises in the next two to four years.
ADAPT’s survey of 170 Chief Digital Officers (CDOs) reveals that data-driven decisions pose a significant challenge in achieving a world-class employee experience.
Chief Digital Officers’ priorities from 2021 to 2023 display this transition.
- 2021: Operational effectiveness
- 2022: Attracting and retaining talent
- 2023: Cyber security
With the rapid uptake in generative AI tools, ADAPT expects next year’s priority to be becoming a data-driven organisation.
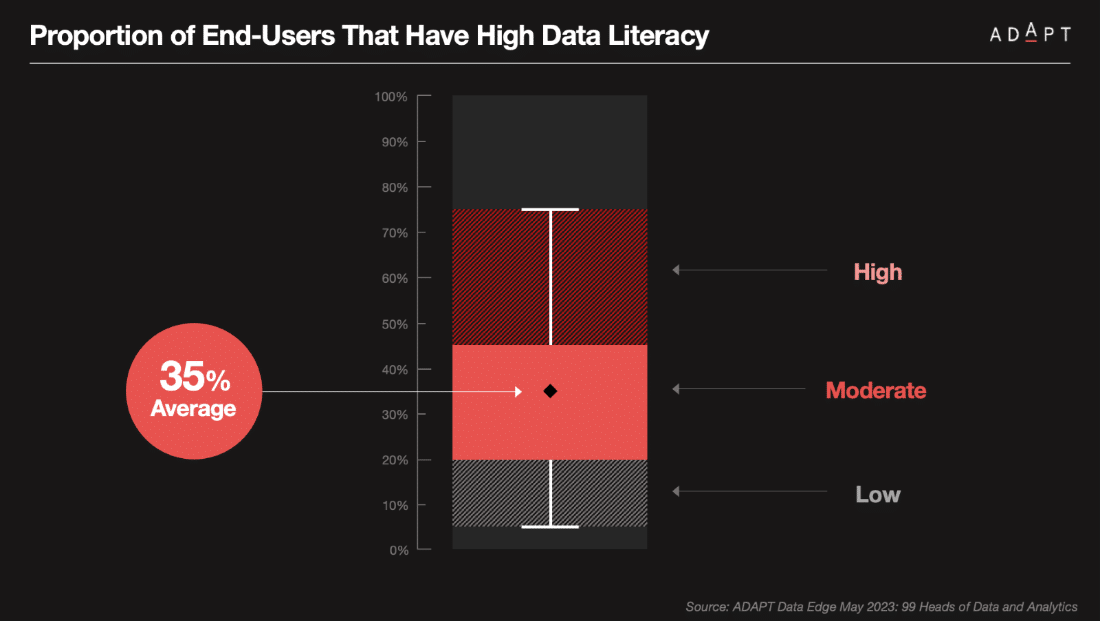
Only 35% of users have high data literacy, which limits the creation of dashboards and data-driven decisions.
Low data literacy hampers data democratisation and impedes access to insights through tools like CoPilot and ChatGPT.
Amazon, determined not to fall behind in the fiercely competitive AI race, is launching a new program aimed at supporting customers and partners focused on generative AI.
Called the AWS Generative AI Innovation Centre, the program will put $100 million to connect AWS-affiliated data scientists, strategists, engineers, and solutions architects with customers and partners to accelerate enterprise innovation and success with generative AI, as stated in Amazon’s press release.
Meanwhile, Cisco is integrating generative AI into its security and collaboration systems to boost productivity and automate tasks. During Cisco Live 2023, the company showcased its use of large language models (LLMs).
Faisal Bhutto, Senior VP of Cloud and Cyber security at Cisco’s partner Calian Group, emphasised AI’s potential in meeting talent demands and countering security threats.
According to ADAPT’s Responsive Generative AI report, reveals significant risks arising from Generative AI training, encompassing:
- Deepfakes and Phishing: Generative AI intensifies the threat of deepfakes and phishing, producing convincing images, videos, texts, and voice recordings that can deceive citizens. The line between reality and misleading content blurs, heightening the potential for disinformation and social engineering (Davenport & Mittal, 2022).
- Malicious Code Injection: Malicious code injections, surpassing security controls (dynamic, static), create vulnerabilities. Lemos (2023) outlines a comprehensive attack sequence employing multiple code generators, potentially breaching systems. A DDoS-like attack floods production environments with extensive new code generated by Generative AI.
- Automated Exploits and Decision-Making Attacks: Automated Exploits utilise brute force on existing vulnerabilities, akin to the global Log4j incident. Decision-making attacks may impact systems like the Osko platform, jeopardising customer and organisational interests through financial loss, regulatory violations, and brand damage. This may involve data alteration, synthetic data injection, and fraudulent activities.
These risks manifest in various scenarios, involving deception with far-reaching financial, identity, and brand consequences. Deception can target job or loan applications, infrastructure pipelines, and malpractice cases involving manipulated data.
Data Leaders must collaboratively assess these risks with the CISO and Chief Risk Officer before initiating Generative AI projects, ensuring informed decision-making and risk mitigation.
However, there is a concern about potential harm caused by AI to stakeholders without proper risk controls.
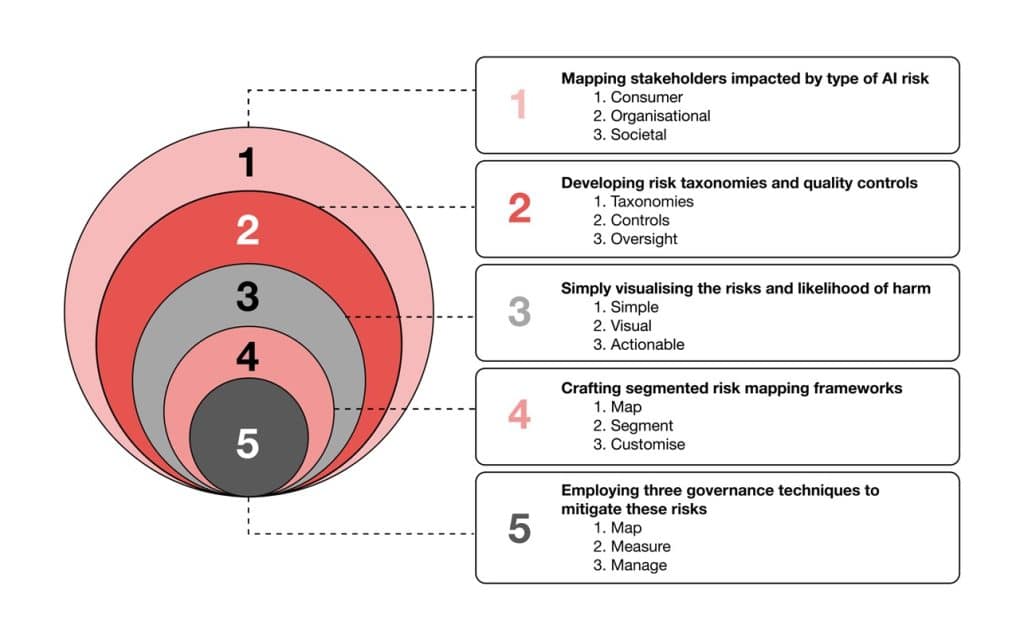
According to ADAPT’s Handbook for Surviving the AI Apocalypse, organisations can mitigate risks by:
- Identify AI risks based on the stakeholders impacted.
- Utilise risk taxonomies and quality controls.
- Use visualisations to understand the likelihood of harm.
- Develop stakeholder-specific risk mapping frameworks.
- Implement an agreed AI governance model.
- Ensure continuous discipline as AI training, implementation, and associated risks evolve.
- Regularly examining risks, such as model bias and ethical issues, which are vital to meeting stakeholder expectations.
Despite the challenges, generative AI continues to be a top investment choice, significantly influencing emerging technologies such as AWAs and conversational AI.
2. Rampant cyber threats lead to organisations embracing MFA, enhanced data security, and sufficient budget allocation
Data breaches and other cyber crimes have plagued Australian organisations in vast proportions since the start of the pandemic.

According to ADAPT’s extensive 2023 study involving 511 Australian executives, it was found that one in four organisations experienced disruptions caused by cyber incidents in the past 12 months.
These incidents included website outages and the unauthorised release of personally identifying information. Barracuda Networks’ 2023 spear phishing trends report corroborates ADAPT’s findings, revealing that 46% of Australian organisations fell victim to spear phishing in 2022.
Globally, spear-phishing attacks accounted for 66% of all breaches, despite comprising only 0.1% of email-based attacks.
These attacks have resulted in infected machines, stolen sensitive data, and direct monetary losses for organisations. Even the critical healthcare sector did not escape from these attacks. SOTI’s research reveals that 78% of global healthcare providers offering frontline services have experienced at least one data breach since 2021.
In Australia, 91% of healthcare IT professionals are concerned about patient record security, and accidental data leaks from employees have seen a continuous increase year-on-year.
Additionally, 66% of Australian healthcare organisations experienced planned or accidental data leaks, and 63% have encountered data breaches from external sources or DDoS attacks.
The problem is so severe that CIOs, CISOs, Digital leaders, and Infrastructure leaders unanimously ranked cyber security as their most pressing business priority in 2023.
The decision is a practical one, as revealed by GetApp, which found that being passive in these cases could lead to significant legal problems and loss of public trust.
According to the survey, over 50% of Australian consumers would consider legal action against companies responsible for leaking their data. Additionally, 41% of consumers would cease doing business with a company involved in a data breach, and 49% have already stopped buying from such companies.
These results highlight the need for more precise and accurate data privacy policies.
Trustworthiness is crucial for consumers when sharing personal information, and many feel that companies must take concrete measures to ensure the security of their data.
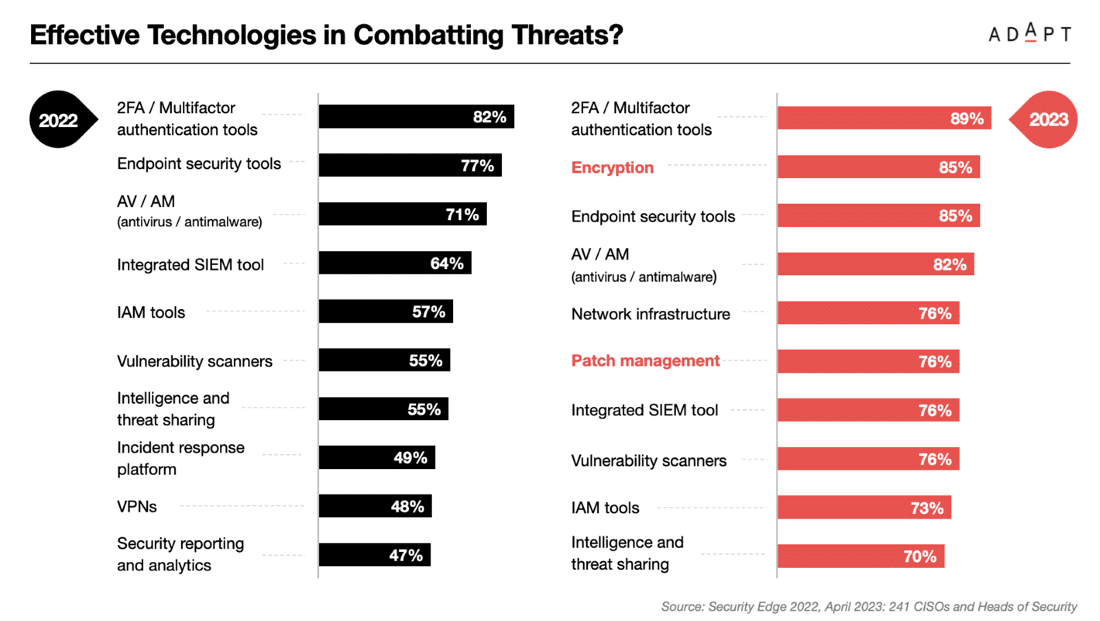
Based on ADAPT’s survey of 241 Australian CISOs, it was revealed that multifactor authentication (MFA), a key component of Zero Trust Security systems, is considered the most effective technology in combating such threats.
Close behind, encryption ranked as the second most effective technology, mainly due to its focus on data security and protection of sensitive information.
In the 2022 survey, the primary obstacle to cyber security was the prevalence of too many manual processes operated through outdated legacy technology, which did not align with the demands of digital workflows.
However, a shift occurred in 2023, as data security emerged as the most significant security threat, surpassing ransomware incidents, according to insights from 242 surveyed CISOs.
This change is attributed to higher adoption rates of MFA and increased investment in security through Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions.
Nonetheless, concerns persist regarding social engineering leakage, highlighting the importance of enhancing staff cyber security awareness and training.
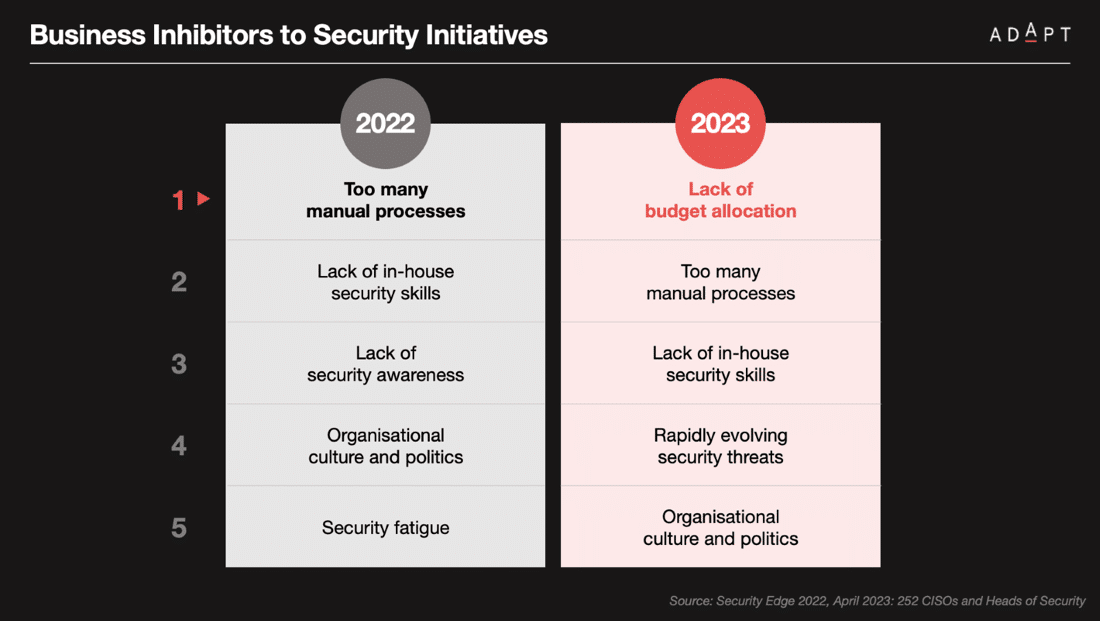
Interestingly, in 2023, the most prominent business inhibitor to security initiatives shifted from manual processes to insufficient budget allocation, as observed in ADAPT’s study involving 252 CISOs.
Gaining support for security initiatives and tools continues to be challenging, and CISOs view their success in their ability to keep security-related matters out of the public’s attention.
ADAPT also raises pertinent questions about the adequacy of budget allocation for CISOs especially considering the rising expectations to protect organisational data.
Despite the increased pressure on businesses to secure assets, the study suggests that funding for cyber security has not seen a proportional increase.
3. The Federal Budget 2023 embraces tech advancements, addressing cloud migration challenges and boosting digital economy
The Federal Budget 2023 focuses on upgrading technology to address the cost of living crisis and improve economic growth and job creation.
The budget allocates $162.4 million over four years for these initiatives to enhance the country’s financial stability and resilience.
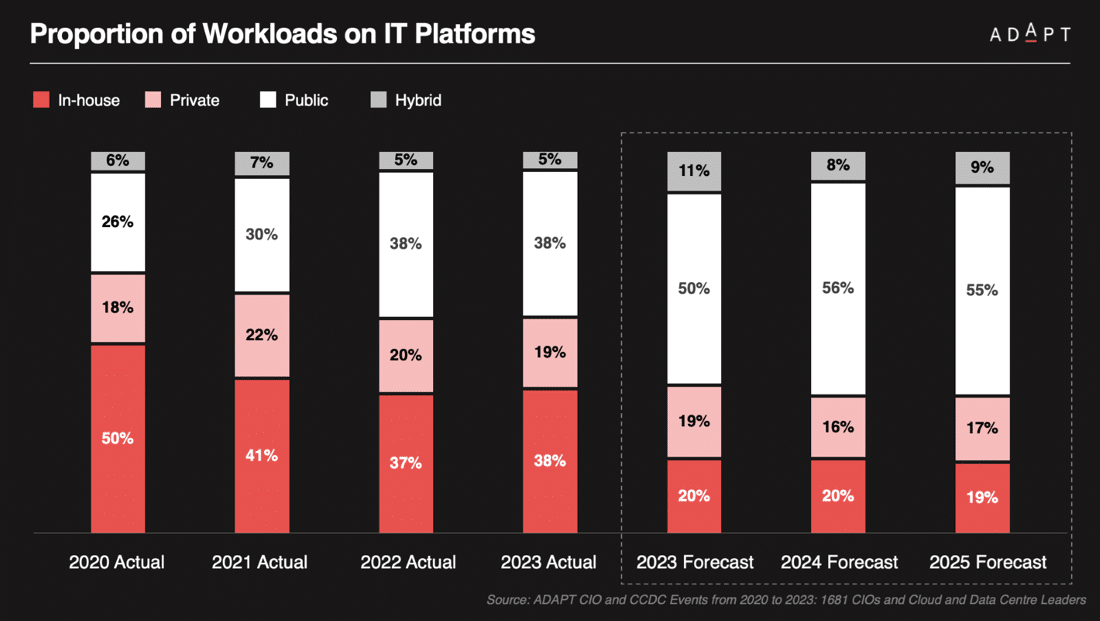
According to ADAPT’s Cloud Migration Study, which surveyed over 1,000 digital transformation leaders, the share of IT storage and processing performed by public cloud environments is predicted to rise to 47% by 2023, indicating a significant increase from the previous year.
The research highlights challenges during cloud migration, including legacy systems, architectural complexities, compliance issues, lack of internal cloud expertise, data security concerns, and higher-than-expected migration costs.
These challenges resonate with the insights from the Federal Budget 2023, which emphasises the importance of technology upgrades and innovation for the government and business sectors.
The budget allocates funds for critical technology development, including cyber security, reflecting the government’s commitment to protect citizens and infrastructure amidst cloud migration challenges.

Additionally, the research reveals that 18% of organisations now use more than five public cloud environments, and 9% are reconsidering their cloud strategies and migrating workloads back from the public cloud.
These findings indicate a reevaluation of cloud strategies in the market. The complexity of multi-cloud environments and interoperability challenges has prompted some organisations to choose in-house colocation or private clouds, necessitating a shift in cloud migration strategies.
The research suggests that cloud providers and technology leaders need to make adjustments to address these challenges.
Cloud providers should collaborate with other vendors to offer customers better visibility over their assets in multi-cloud environments.
On the other hand, technology leaders are advised to adopt an ‘outcome-first’ mindset, carefully assessing the best options for their workloads before fully committing to public cloud migration and ensuring proper auditing of assets and frameworks for successful cloud initiatives.
In addition to the cloud-related insights, the 2023-24 federal budget includes funding for various technology projects, with an estimated total spending of $3.7 billion over the next four years.
Notable projects include:
- Investments in the National Disability Insurance Agency (NDIA).
- Modernising My Health Record.
- Funding for the Australian Digital Health Agency (ADHA).
Furthermore, industry professionals express their views on the revised employee share scheme, the need for more visible pathways to tech careers, and expedited skilled visa processes for tech workers, reflecting concerns about the current state of the ‘Ideas Boom’ and the National Science Innovation Agenda.
In general, the federal government’s commitment to boosting the digital economy strategy by allocating an additional $130.1 million, with a focus on cyber hubs, data rights, and digital policies, aligns with the evolving landscape of cloud migration challenges and technological advancements.
These initiatives aim to strengthen Australia’s position as a leader in the data and digital economy by 2030.
4. Maximising cloud services assists teams in collaborating effectively, optimising costs, and achieving long-term savings.
Recent headlines highlight the substantial investments made by major tech companies in cloud services, as well as the emergence of partnerships between these tech giants.
Furthermore, cloud computing capabilities have witnessed significant developments, further affirming the growing importance of cloud-based solutions in the IT landscape.
A noteworthy trend that has garnered attention is the temporary halt in moving workloads to the cloud, often referred to as ‘cloud repatriation’.
This phenomenon raises questions about the reasons behind this strategic shift. One possible explanation is that some organisations are discovering that the cloud is not delivering on expected financial performance.
To address this issue, cloud engineers are advised to collaborate more closely with CFOs to ensure more accurate forecasting of cloud-related expenses.
Despite the challenges, it is important to recognise the benefits of cloud migration. When executed correctly, it can result in cost-effective, resilient, and secure frameworks that are scalable to meet evolving business needs. However, it is essential to recognise that scalability does not always have to be a constant requirement.
Organisations that have been billed based on hourly rates for cloud usage have encountered unexpected cost blowouts. Instead, opting for longer contracts with a stable load can be a more prudent approach.
Furthermore, loyalty to a cloud vendor can result in significant long-term savings for both organisations and tech vendors. Establishing long-term partnerships ensures a steady stream of annuity, guaranteeing income for vendors while providing organisations with predictable and lower costs.
In summary, cloud services and partnerships continue to play a crucial role in the IT industry, with major tech companies investing heavily in this domain.
However, the pause in cloud migration and the need for improved financial forecasting underscore the importance of careful planning and collaboration between cloud engineers and CFOs.
By architecting cost-effective, resilient, and secure frameworks and considering stable load contracts, organisations can optimise their cloud utilisation and achieve long-term cost savings.
Conclusion:
As executive leaders, it’s crucial to stay informed about transformative technologies that can shape the future of our organisation.
Cloud migration and generative AI adoption have the potential to revolutionise how we operate. Understanding their intricacies will help us identify opportunities and challenges, allowing for seamless integration into our existing systems and processes.
Moreover, embracing these technologies can significantly impact our cost optimisation efforts. By making informed decisions about investments and resource allocation, we can achieve long-term savings and enhance our financial stability.
We cannot overlook the importance of cyber security in today’s digital landscape. A deeper understanding will enable us to identify potential vulnerabilities and implement robust measures to safeguard our assets, data, and most importantly, our customers’ trust.
Furthermore, government support for digital transformation initiatives offers opportunities for funding, grants, and incentives. As executive leaders, we can leverage this support to drive innovation and fuel growth within our organisation.
Compliance with government policies and regulations related to data privacy, cyber security, and AI adoption is paramount. A thorough understanding will help us navigate the regulatory landscape and avoid potential legal and financial risks.
Lastly, grasping the potential of cloud migration, generative AI, and emerging technologies can provide us with a competitive edge.
By staying ahead of our competitors and effectively implementing these innovations, we position ourselves for success in an ever-evolving business landscape.